
Air Curtain Selection Guide for GCC Buildings
This air curtain selection guide is written for MEP consultants, facility managers, and HVAC contractors working across the GCC—UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, and Kuwait. You’ll find essential sizing rules, specification checklists, commissioning steps, and installation best practices to choose the right unit for your doorway, climate, and application. We also include quick links to the Cross‑Flow vs Centrifugal explainer and Installation Best Practices, plus worked examples and ready‑to‑copy spec language to streamline submittals.
Selection at a Glance
When performing an air curtain selection for GCC projects, use this quick decision path before deep‑diving into specs:
Doorway type (swing/auto‑sliding/roll‑up/revolving) and clear width.
Mounting height → up to ~3.5 m (cross‑flow) or ~4–8 m (centrifugal/industrial).
Traffic intensity → light, medium, or heavy/continuous (people, carts, forklifts).
Application → retail/hospitality/healthcare vs industrial/logistics vs cold room.
Model family → slim cross‑flow for FOH spaces, high‑velocity centrifugal for docks, cold‑room series for freezers.
Controls → door interlock, staged speeds/VFD, BMS integration, seasonal presets.
Acoustics & aesthetics → recessed kits, architectural fascias, dB(A) caps for guest/patient areas.
Rule of thumb: Always size to fully cover the entire door width and meet floor‑level velocity requirements at the threshold; a partial jet equals partial protection.
Core Sizing Parameters
Proper air curtain selection depends on the following parameters:
1) Door Height & Width
Width determines unit length or multi‑section arrays; keep a continuous nozzle line (no gaps).
Height determines jet type: cross‑flow works best up to ~3.5 m; centrifugal for 4–8 m; add side columns only when lintel is impossible.
2) Air Velocity Targets (typical design values)
Nozzle discharge velocity: 8–18 m/s depending on height/pressure.
Floor‑level velocity at threshold:
Comfort/energy separation: ~2.0–2.5 m/s
Insect control (F&B/healthcare): ~2.5–3.0 m/s
Cold rooms/freezers: maintain seal with ≥2.5 m/s at sill
3) Air Volume (m³/h) & Throw
Ensure a coherent jet from discharge to floor, with uniform distribution across width; verify throw exceeds door height by 10–20% margin.
4) Nozzle Angle & Jet Uniformity
Start with 0–10° outward tilt; increase slightly if wind/stack effect pushes jet back. Avoid angles that cause jet detachment from the opening.
5) Mounting Options
Horizontal above lintel (standard), recessed for premium aesthetics, or vertical side‑mount where lintel depth is limited; maintain unobstructed intake and discharge.
6) Electrical & Controls
EC motors/VFD for efficiency & fine speed control; door microswitch; BMS dry contact/Modbus; staged speeds for peak/off‑peak; interlock with automatic doors for synchronized start/stop.
7) Acoustics
Hospitality/healthcare targets typically ≤55–60 dB(A) at 1–3 m; specify test conditions and measurement distance.
8) Environment & Pressure
Consider prevailing winds at entrances, building stack effect, and pressure differentials created by exhaust systems; upsize velocity or adjust angle accordingly.
Application‑Specific Guidance
Retail & Malls
Goal: Comfort, energy savings, quiet operation with doors open.
Spec: Slim cross‑flow, recessed where possible; 2.3–3.5 m height; low dB(A) and architectural fascia; integrate with storefront lighting lines.
Hospitality & Restaurants
Goal: Guest comfort + insect control at entrances and kitchen pass‑throughs.
Spec: Cross‑flow with floor velocity ≥2.5–3.0 m/s; quiet operation; grease‑resistant finishes BOH; door interlock on swing/slider.
Healthcare
Goal: IAQ and hygiene at lobbies, pharmacies, and clean corridors.
Spec: Quiet cross‑flow with enhanced filtration; stable jet to minimize ingress; optional HEPA pre‑screens at intake where required.
Industrial & Warehouses
Goal: Reduce energy loss and dust ingress at high doors and loading bays.
Spec: Centrifugal industrial units; mounting 4–8 m; robust casing; high nozzle velocity; forklift‑safe clearances; BMS integration.
Cold Storage
Goal: Prevent cold loss, condensation, and icing.
Spec: Dedicated cold storage air curtain models; maintain ≥2.5 m/s at floor; humidity management; consider door heaters/anti‑frost sequencing.
Model Family Map (Klima Global Range)
In your air curtain selection, match application to Klima Global’s Airblade range:
Cross‑Flow Series (Retail/FOH): Model K, G, O, B, I – slim, quiet, ideal up to ~3.5 m.
Centrifugal/Industrial (BOH/Docks): Model A, A2, G2, L, L2 – high velocity for large openings up to ~6–8 m.
Cold Room Series: purpose‑built Cold Room Air Curtain for freezers/coolers.
Heated Options: Model E2 (PTC Heating) and Water‑Heating Cross‑Flow for mixed or winter conditions.
Tip: Match door height/width to catalogue performance tables to confirm discharge and floor velocities; check motor kW and current for circuit sizing.
Step‑by‑Step Sizing Procedure
Follow this air curtain selection process:
Measure the opening: clear height, width, lintel depth; door type; proximity of signage/lighting; allowable recess space.
Classify the application: retail/hospitality/healthcare vs industrial vs cold room; define IAQ/insect/energy priorities.
Set performance targets: energy separation only or also insect control/IAQ; define floor‑level velocity and dB(A) limits.
Pick the jet type: cross‑flow (≤3.5 m) or centrifugal (4–8 m); choose cold‑room series for freezers.
Select length & quantity: single unit or multi‑section array to cover full width; ensure continuous nozzle line and common control.
Choose controls: door interlock, BMS, staged speeds/VFD, thermostat (heated models), seasonal presets (summer/winter).
Aesthetics & acoustics: recessed kits, architectural fascia, anti‑vibration isolation, and dB(A) limits for FOH/healthcare.
Finalize electrical & mounting: supply, breakers, cable routing; bracket pattern; minimum clearances; service access; condensate management for cold rooms.
Commissioning: verify discharge & floor velocities, adjust nozzle angle, confirm door interlocks, balance speeds for off‑peak/peak, and record settings in the O&M.
Worked Example – Storefront in Dubai (3.2 m x 2.8 m)
Opening: 2.8 m clear width, 3.2 m height, automatic sliding doors; premium mall.
Application: Retail comfort + dust exclusion; dB(A) target ≤55 at 2 m.
Model class: Cross‑flow, recessed fascia; two modules to cover 2.8 m (no gaps).
Design: Discharge 12–14 m/s; floor velocity target 2.3–2.5 m/s; nozzle angle 5° outward.
Controls: Door interlock + 3‑stage speed; BMS dry contact; nighttime setback speed.
Result: Stable entrance comfort with doors open; reduced HVAC load and improved customer experience.
Specification Checklist
Use this air curtain selection checklist:
Performance
Rated air volume (m³/h): ____
Nozzle discharge velocity (m/s): ____
Floor‑level velocity at threshold (m/s): ____
Jet angle (°): ____
Coverage width (mm): ____
Throw (m): ____
Construction
Casing: steel/aluminum; finish color RAL: ____
Access: service panel/filter access front/bottom
Filter class (where applicable): ____
Ingress protection (IP): ____
Motors & Fans
EC motor/VFD; duty cycle: continuous
Bearings: sealed; design life: ____
Input power (kW) / FLA (A): ____
Controls & Integration
Door interlock microswitch: yes/no
Speed stages: 2/3/variable
BMS: dry contact/Modbus
Heated unit control: thermostat/high‑limit safety
Seasonal presets & timers: yes/no
Compliance & Docs
GCC electrical standards; ASHRAE/Estidama alignment
Submittals: datasheet, wiring diagram, O&M, commissioning sheet
Test data: velocity profile at threshold; dB(A) at stated distance
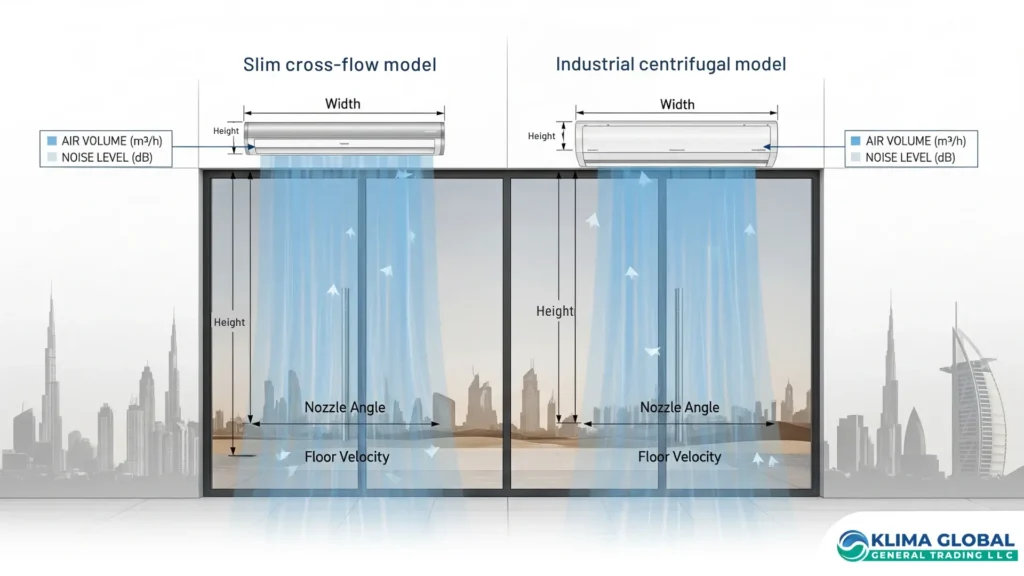
Cross‑Flow vs Centrifugal
For accurate air curtain selection, understand the difference:
Cross‑Flow: slim, quiet, energy‑efficient; best for ≤3.5 m retail, hospitality, and healthcare doors; ideal for recessed architectural treatments.
Centrifugal: high‑pressure/velocity for 4–8 m industrial doors, docks, and busy portals; robust housings and serviceable components.
Read the companion article: [Cross‑Flow vs Centrifugal – Which to Choose?]
Installation Best Practices
Correct installation is critical for effective air curtain selection:
Full‑width coverage: no blind spots; align multiple sections tightly; use joining kits/seals.
Mount tight to lintel: minimize recirculation; avoid setbacks and signage blocking the jet; protect intake from soffit lights.
Tune the jet: start at 0–10° outward tilt; verify floor velocity; adjust stages/VFD for peak hours; verify with anemometer at multiple points across width.
Seal & level: maintain a straight, continuous nozzle line across the span; shim where needed.
Maintain: routine filter cleaning, velocity checks, fan/motor inspection; record readings in maintenance log.
See: [Air Curtain Installation Best Practices]
Controls Strategies by Space Type
Retail/Hospitality: door‑open interlock + 2–3 speeds; quiet mode off‑peak; BMS occupancy schedule.
Healthcare: constant low‑noise speed; boost on door open; alarms to BMS on fault.
Industrial: VFD ramp on door cycle; dock door contacts; auto‑shutdown on long closures.
Cold Rooms: interlock with door heaters/defrost; anti‑frost logic; humidity sensors optional.
GCC‑Specific Considerations
In GCC, air curtain selection requires considering:
Heat, wind & dust: size for higher nozzle velocity; consider enhanced filtration/IP protection; specify corrosion‑resistant finishes in coastal Qatar/Oman.
Energy codes & sustainability: align with DEWA, Estidama, Saudi Vision 2030, Qatar Vision 2030; document kWh savings in O&M for ESG reporting.
Serviceability: prioritize models with strong local parts/service coverage across UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, and Kuwait; include spare filters/fans in BOQ.
Pre‑Commissioning & Handover Checklist
Electrical checks complete; rotation and balance verified.
Jet alignment set; threshold velocity measured at 3–5 points; readings meet spec.
Noise level recorded with meter; within limits.
BMS/door interlocks tested; event logs confirmed.
O&M delivered with as‑built settings; maintenance schedule issued.
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Undersized width → leaves gaps; always span full opening.
Mounting too high for cross‑flow → choose centrifugal above ~3.5 m.
No jet tuning → verify floor velocity, adjust angle/speed.
Blocked intake/discharge → keep soffit lights/signage clear.
Ignoring acoustics → set dB(A) caps for hotels/clinics.
Conclusion
With the right sizing, velocity targets, and controls, an air curtain will cut energy loss, improve comfort/hygiene, and protect processes in GCC buildings. Use this air curtain selection guide to match model families to your door height, traffic, and application—and follow the best‑practice install & commissioning checklists to lock in performance.
Need help selecting a model for UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, or Kuwait? Contact Klima Global for engineering assistance, submittal‑ready specs, and on‑site commissioning support.
FAQs: Air Curtain Selection Guide
How do I decide between Cross-Flow and Centrifugal for my entrance?
Use Cross-Flow for most hotel/office doors at ~2.3–3.0 m mounting height where you want slim aesthetics and low noise; use Centrifugal for >3.5 m mounts, wind-exposed entrances, or wider spans needing higher pressure to hold the jet at the floor. Always match unit width to door width, start with a 0–10° nozzle angle, and verify threshold velocity with an anemometer.
What design inputs do I need before I can size an air curtain correctly?
Gather: clear door width, mounting height, door type (sliding/swing/revolving), cycle frequency, indoor/outdoor temperature and pressure/wind exposure, any insect control or cold-room requirement, available power, and BMS/door sensor readiness. These determine width, type (cross-flow vs centrifugal), target floor velocity, and control strategy.
What threshold velocity should I aim for in different use cases?
Premium lobbies/offices: ~2.0–2.5 m/s (comfort + hygiene without draft complaints)
Retail/FOH with higher traffic or insects: ~2.5–3.0 m/s
Cold rooms/industrial bays: often ≥2.5 m/s (confirm with process/food-safety needs)
Set the nozzle angle during commissioning to keep the jet coherent at the sill line under real stack/wind conditions.
In GCC projects, should I prioritize heated models or smarter controls for comfort?
In the GCC, most entrances perform best with unheated units plus smart control: door sensors to ramp up only on door open and BMS schedules aligned to access hours. Heated options (e.g., PTC or water heating) are niche—used for over-cooled vestibules or special comfort complaints. Prioritize correct sizing, nozzle tuning, and interlocks before adding heat.
What are the most common selection mistakes—and how do I avoid them?
Undersized width → edge leakage/whistling. Match unit width to door width.
Wrong type for height → weak floor velocity. Use centrifugal above ~3.5 m.
Starved intake → hiss/tonal noise. Provide soffit/signage clearance.
No control logic → always-high speed/noise. Add door interlock + BMS schedule.
Skipping commissioning → poor jet shape/drafts. Set nozzle 0–10°, verify floor velocity.
No maintenance plan → rising noise/performance drop. Follow monthly/quarterly tasks.
Get Customized Air Curtains for your Project!
Share this post
Related Posts


Best Air Curtain Supplier in Saudi Arabia | Buyer’s Guide

Low Noise Air Curtain | Silent Air Curtains for Hotels & Offices

The Ultimate Guide to Air Curtains in the Middle East

Air Curtain Maintenance Guide –Checklist, Service & Lifespan

Air Curtain Installation Guide – Mounting, Sensors & BMS
Latest Posts

Best Air Curtain Supplier UAE | 2025 Buyer’s Guide

Best Air Curtain Supplier in Saudi Arabia | Buyer’s Guide

Low Noise Air Curtain | Silent Air Curtains for Hotels & Offices

The Ultimate Guide to Air Curtains in the Middle East

Air Curtain Maintenance Guide –Checklist, Service & Lifespan

Air Curtain Installation Guide – Mounting, Sensors & BMS
