

Air Curtain Installation: Best Practices for GCC Buildings
This field‑ready air curtain installation guide is written for MEP contractors, HVAC integrators, and facility teams operating in the GCC—UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, and Kuwait. You’ll learn how to survey the doorway, choose the right mounting height and orientation, wire controls, integrate with door sensors/BMS, and commission the unit for verified performance. Follow these best practices to ensure your air curtain installation delivers comfort, hygiene, and measurable energy savings.
New to door-jet basics? Start with our comprehensive Air Curtains Guide before you install.
Pre‑Install Survey & Site Readiness
Thorough preparation is the foundation of every successful air curtain installation.
Opening & Door Type: Record clear opening height/width, lintel depth, and door style (swing, automatic sliding, roll‑up, revolving).
Obstructions: Identify signage, bulkheads, sprinkler heads, and lighting that may block the intake or discharge.
Environment & Pressure: Note wind exposure, stack effect, and nearby exhaust/pressurization systems. This informs jet angle and velocity during installation.
Electrical: Verify dedicated circuits, breaker sizing, and cable routes; confirm earthing and isolator locations.
Access & Safety: Plan lifts/scaffolding, out‑of‑hours work, and cordoned areas for public sites in malls/hotels.
Pro tip: Capture photos and dimensions in a pre‑install checklist template so the air curtain installation crew arrives with the correct brackets, anchors, and cable lengths.
For step-by-step sizing logic, use the Air Curtain Selection Guide, then compare options by height in the Air Curtain Comparison — Cross-Flow vs Centrifugal.
Mounting Height & Orientation
Mounting decisions determine jet coherence and threshold velocity—core outcomes of any air curtain installation.
Cross‑flow units perform best at ~2.3–3.5 m. They’re slim and ideal for storefronts, hotel lobbies, cafés, and clinics.
Centrifugal/industrial units suit ~4–8 m doors and loading docks, offering higher static pressure and throw.
Horizontal above lintel is preferred; recessed mounting enhances aesthetics in premium FOH spaces; vertical side‑mount is a last resort when lintel space is unavailable.
Full‑width coverage is mandatory. Multi‑section arrays must be joined without gaps so the nozzle forms one continuous line.
Nozzle angle: Start at 0–10° outward. Fine‑tune after commissioning readings at the threshold; increase angle if wind or stack effect deflects the jet.
Document all mounting choices in the air curtain installation method statement for consultant approval.
For quiet hotel and office lobbies at ≈2.3–3.0 m mounts, shortlist Model I and Model K; for >3.5 m or wind-exposed portals, consider Model A, Model A2, or Model L2.
Structural & Fixing Best Practices
Robust fixings keep the unit stable and quiet over its service life—another hallmark of quality air curtain installation.
Use appropriate anchors for masonry/steel/concrete; confirm load paths for dynamic forces.
Include vibration isolation pads/strips to reduce dB(A) in hospitality and healthcare settings.
In coastal Qatar, Oman, and Bahrain, prioritize corrosion‑resistant hardware and coatings.
Maintain unobstructed intake clearances (typically ≥150–200 mm) and straight discharge exits.
For design-led entrances where the unit should ‘disappear,’ explore premium casings like Model O and Model G.
Electrical, Controls & BMS Integration
Controls separate good from great air curtain installation outcomes.
Door Interlocks: Use a microswitch/magnetic contact or signal from the automatic door controller (open = run; closed = stop or setback).
Speed Control: Provide staged speeds or VFD/EC motor control to handle peak traffic and off‑peak.
BMS Integration: Expose run/stop, fault, and speed status via dry contact/Modbus; schedule occupancy modes and seasonal presets.
Heated Units: For PTC/water‑coil models, wire thermostats, actuators/valves, and high‑limit safety cut‑outs per manufacturer instructions.
Safety & Compliance: Label isolators, confirm earthing continuity, and document wiring diagrams in the handover pack.
These integration steps allow your air curtain installation to work in sync with HVAC and access control systems, minimizing energy waste.
To cut runtime and noise while improving comfort, implement door interlocks and BMS staging as outlined in Energy Saving Air Curtain.
Commissioning Procedure
Commissioning verifies that the air curtain installation performs as designed.
Rotation/Balance: Confirm correct fan rotation and absence of abnormal vibration.
Threshold Velocity Test: Using an anemometer, record readings at 3–5 points across the doorway at floor level. Typical targets:
Comfort/energy: ~2.0–2.5 m/s
Insect control (F&B/healthcare): ~2.5–3.0 m/s
Cold rooms/freezers: ≥2.5 m/s sustained at sill
Nozzle Tuning: Adjust angle (0–10° outward) and speed stages/VFD to hit targets under real operating conditions (doors open).
Noise Check: Measure dB(A) at a stated distance (e.g., 2 m) and compare to spec limits for FOH areas.
Controls/BMS: Prove door sensor logic, alarms, and point mapping; confirm time schedules and setback modes.
Handover: Record final settings, velocity/Noise logs, and provide O&M with maintenance schedule.
A documented commissioning record is the best insurance that your air curtain installation will hold performance over time.
Multi‑Section & Wide Openings
Many GCC entrances exceed single‑unit widths; this is where disciplined air curtain installation matters most.
Alignment: Level and plumb all sections before final tightening.
Sealing: Use joining kits and gaskets to eliminate leakage between sections.
Common Control: Link modules to a single controller so speeds and modes change together.
Uniformity: Verify velocity at section joints during commissioning; correct any low spots with angle/speed trims.
Special Applications
Different use‑cases require tailored air curtain installation details.
Cold Rooms & Food Logistics
Maintain ≥2.5 m/s at the sill to resist warm, humid air.
Coordinate with door heaters/defrost cycles and humidity control.
Add anti‑frost logic and routine de‑icing checks in the O&M.
Industrial Loading Docks
Choose high‑velocity centrifugal models at 4–8 m mounting heights.
Interlock with dock door controllers; ensure forklift clearances and impact protection.
Consider wind breaks or vestibule geometry if cross‑winds are severe.
For wide shutters, wind-exposed bays, or vertical pairs, see the pressure-capable options in Industrial Air Curtain (Centrifugal Type).
Hospitality & Healthcare
Prioritize low‑noise operation and recessed fascias.
Upgrade filtration where IAQ is critical; log velocity and dB(A) in the commissioning report.
For patient-facing entrances with stricter acoustic and hygiene expectations, review Hospital Air Curtain – GCC.
Maintenance & Service Intervals
Planned maintenance sustains the benefits of your air curtain installation.
Monthly/Quarterly: Clean filters/grilles; check for debris; verify fasteners; visually inspect wiring/terminals.
Quarterly: Re‑measure threshold velocity; compare to baseline; adjust angles/speeds if needed.
Annually: Electrical inspection, bearing checks, vibration/noise audit; refresh BMS schedules.
Spares: Stock filters and critical fan/motor components for high‑traffic sites.
If noise rises or barrier performance drifts, use the symptom-to-cause tables in the Air Curtain Maintenance Guide.
Common Installation Mistakes (and Fixes)
Avoid these pitfalls that undermine air curtain installation performance:
Undersized width: Any gap creates a leak path—always span the full opening.
Mounting too high for cross‑flow: Above ~3.5 m, specify centrifugal units.
Blocked intake/discharge: Move signage/lighting; keep clear airflow paths.
No door interlock: Running constantly wastes energy; enable open/run logic.
Skipping velocity tests: Commission with an anemometer, not by feel.
Conclusion
A professional air curtain installation protects comfort, hygiene, and energy budgets in GCC buildings. By surveying the site, selecting the right mount/orientation, integrating door sensors/BMS, and commissioning to verified velocity and noise targets, you’ll deliver reliable results in malls, hotels, clinics, warehouses, and cold rooms.
Ready to specify? Browse sizes, finishes, and accessories across the Air Blade – Air Curtain range.
Need expert support for air curtain installation in UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Bahrain, or Kuwait? Contact Klima Global for site surveys, engineering selection, and turnkey commissioning.
Frequently Asked Questions!
What site measurements do I need before ordering and installing an air curtain?
Collect a complete entrance survey so sizing and mounting are correct the first time:
Door width & clear opening (mm) – match unit width to avoid edge leakage/whistling.
Mounting height (finished floor to header underside) – confirms cross-flow vs centrifugal selection.
Header depth & soffit clearances – ensure the intake isn’t choked by bulkheads/signage.
Door type & operation – sliding, swing, or revolving; cycle frequency; wind exposure.
Power supply (V/Ph/Hz) & isolator location – safe, dedicated electrical feed.
BMS availability – run/stop, speed, fault points; door sensor interface.
Environmental factors – wind tunnels, stack effect, nearby exhausts, lobby pressure.
How high should I mount the unit, and what nozzle angle should I start with?
For most hotel/office entrances, mount cross-flow models at ~2.3–3.0 m; use centrifugal models when mounting >3.5 m (check model datasheets).
Start with a 0–10° outward nozzle angle; fine-tune during commissioning to hit the floor line without bounce-back.
Target threshold velocity at the floor of ~2.0–2.5 m/s (comfort/hygiene). For insect control or harsher conditions, 2.5–3.0 m/s.
Verify with an anemometer in a 3–5 point grid across the sill and adjust angle/speed as needed.
What electrical and control wiring best practices should I follow?
Provide a dedicated circuit and local isolator adjacent to the unit; follow nameplate current/MCB guidance.
Keep low-voltage door sensor wiring separate from mains; terminate per the control diagram.
If using a VFD/EC drive, route cables per EMC guidelines; earth properly to avoid hum/buzz.
Integrate with BMS for run/stop, speed (or setpoint), and fault; align schedules with access-control hours.
Commission door interlock logic so the air curtain ramps up only on door open; standby speed the rest of the time.
How do I prevent vibration and noise after installation?
Use rigid mounting brackets into solid structure; tighten to torque to avoid panel resonance.
Maintain intake clearance from soffits/signage; starved intakes cause hiss and tonal noise.
Seal gaps between unit and header to stop bypass leakage/whistling.
Align multi-section units so the discharge lip is continuous; avoid steps that induce turbulence.
After cleaning the grille/fan wheel, perform a baseline dB(A) reading at ~2 m and record it for future maintenance comparisons.
What should my commissioning and handover checklist include?
Verify electrical rotation/phase, safety earth, and nameplate current.
Confirm door sensor operation and BMS points (run/stop, speed, fault, status).
Tune nozzle angle and speed to meet the floor velocity target; log readings across the sill.
Record installed dB(A) at a consistent distance in “door open” and “standby” states.
Label the isolator, provide O&M docs, and train staff on routine cleaning and quarterly checks.
Get Customized Air Curtains for your Project!
Share this post
Related Posts


Best Air Curtain Supplier in Saudi Arabia | Buyer’s Guide

Low Noise Air Curtain | Silent Air Curtains for Hotels & Offices

The Ultimate Guide to Air Curtains in the Middle East

Air Curtain Maintenance Guide –Checklist, Service & Lifespan
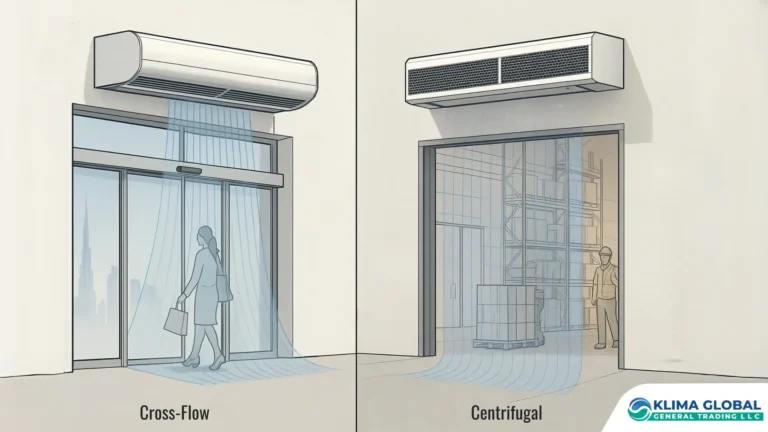
Air Curtain Comparison – Cross-Flow vs Centrifugal
Latest Posts

Best Air Curtain Supplier UAE | 2025 Buyer’s Guide

Best Air Curtain Supplier in Saudi Arabia | Buyer’s Guide

Low Noise Air Curtain | Silent Air Curtains for Hotels & Offices

The Ultimate Guide to Air Curtains in the Middle East

Air Curtain Maintenance Guide –Checklist, Service & Lifespan

Air Curtain Comparison – Cross-Flow vs Centrifugal
